Telematics is the integrated use of telecommunications and informatics technologies to transmit, receive, and analyze data from vehicles in real-time. This system combines GPS technology, onboard diagnostics, and wireless communication to provide comprehensive insights into vehicle location, performance, and driver behavior, enabling more efficient and safer fleet management.
Key Takeaways
- Telematics combines telecommunications and informatics to provide real-time vehicle data and insights.
- Telematics can reduce fuel expenses by up to 30%, significantly impacting fleet operational costs.
- The technology enables various applications, including vehicle tracking, predictive maintenance, and driver behavior monitoring.
- Usage-based insurance programs leveraging telematics are growing at a CAGR of 28.4%.
- Advanced telematics solutions are becoming integral to fleet management across multiple industries.
- Future developments in telematics will incorporate AI and machine learning for even more precise insights and predictions.
Telematics technology powers nearly 775 million vehicles worldwide as of 2023, transforming the landscape of fleet management and vehicle operations.
This rapid adoption rate underscores telematics’ pivotal role in driving operational efficiency, enhancing safety, and reshaping the future of transportation.
Fleet operators who have embraced telematics report up to 30% savings on fuel expenses, demonstrating the technology’s immediate and tangible impact on bottom-line results.
As the industry evolves, telematics continues to unlock new possibilities, from enabling usage-based insurance programs to facilitating predictive maintenance strategies that minimize costly vehicle downtime.
Understanding Telematics: Uniting Telecommunications and Informatics
Telematics represents the convergence of telecommunications and informatics, creating a powerful tool for real-time vehicle data collection, transmission, and analysis. This innovative technology provides unprecedented insights into fleet operations, enabling data-driven decision-making and operational optimization.
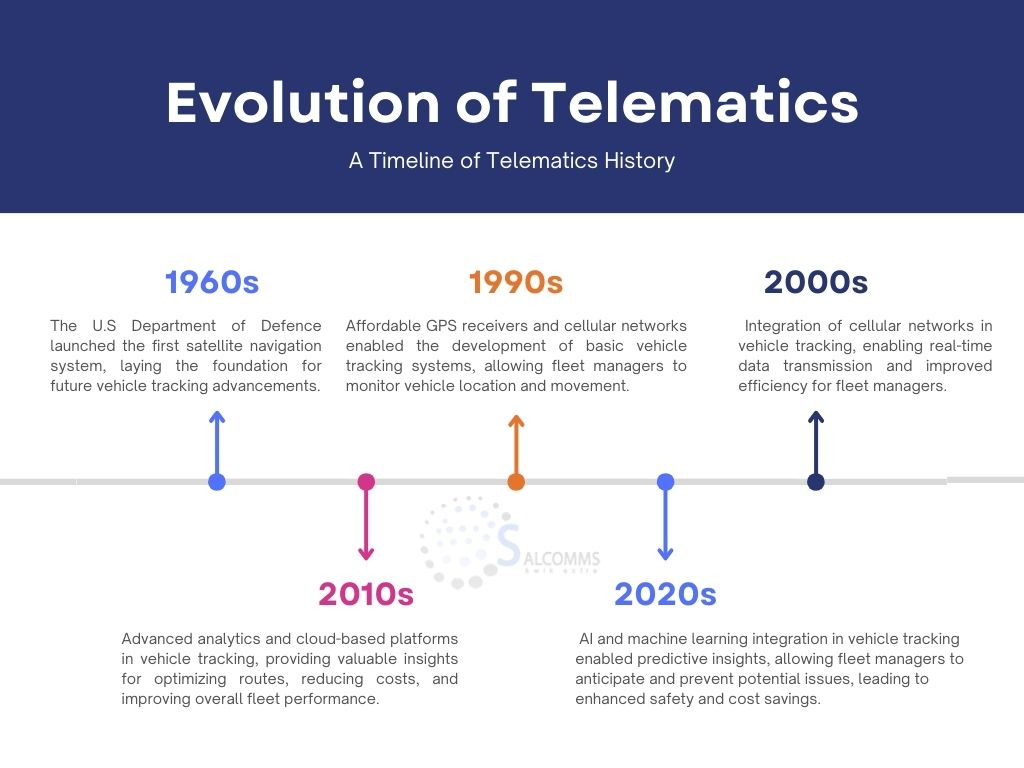
The Evolution of Telematics
It all began with the advent of GPS technology in the 1960s, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that its potential for commercial applications became apparent. Today, telematics has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem of sensors, software, and analytics tools that form the backbone of modern fleet management.
- 1960s: Development of GPS technology
- 1990s: Introduction of basic vehicle tracking systems
- 2000s: Integration of cellular networks for real-time data transmission
- 2010s: Advanced analytics and cloud-based platforms emerge
- 2020s: AI and machine learning integration for predictive insights
The Critical Role in Modern Fleet Management
Telematics has become indispensable in today’s fleet management landscape. It empowers managers to monitor vehicle performance, track driver behavior, and optimize routes in real-time. This level of oversight translates into significant operational improvements, with over 60% of U.S. fleet operators already harnessing the power of telematics to improve their operations.
How Telematics Systems Work: From Data Collection to Actionable Insights
Telematics systems comprise several key components working in harmony to deliver valuable insights.
Core Components of Telematics Systems
- Telematics Devices: GPS units, sensors, and onboard diagnostic systems that collect vehicle data.
- Communication Networks: Utilizing GPRS, 4G, or satellite technology to transmit data.
- Software Platforms: Advanced analytics tools that process and interpret the collected data.
The Data Collection Process
Telematics devices continuously gather a wide array of data points, including:
- Vehicle location and speed
- Engine diagnostics
- Fuel consumption
- Driver behavior (braking patterns, acceleration, etc.)
- Environmental conditions
This data is then transmitted in real-time to centralized servers for processing and analysis.
Turning Data into Action
The true power of telematics lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights. Sophisticated algorithms analyze the collected information to provide:
- Predictive maintenance schedules
- Fuel efficiency recommendations
- Driver performance assessments
- Route optimization suggestions
These insights enable fleet managers to make informed decisions that drive operational efficiency and safety improvements.
Installation and Implementation: Getting Started with Telematics
Implementing a telematics system is a critical step in modernizing fleet operations. The process can vary depending on the specific needs and scale of your fleet.
Installation Methods
- DIY Installation: Suitable for smaller fleets or simpler systems
- Professional Installation: Recommended for larger fleets or more complex integrations
- OEM Integration: Many new vehicles come with built-in telematics capabilities
| Method | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIY | Cost-effective, flexible | May lack advanced features | Small fleets |
| Professional | Comprehensive, expert setup | Higher initial cost | Large fleets |
| OEM Integration | Seamless integration | Limited customization | New vehicle fleets |
Partnerships with OEMs
The telematics industry is seeing increased collaboration with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). By 2023, 87% of all new vehicles in North America were projected to come equipped with embedded telematics systems. This trend is set to simplify implementation and enhance the capabilities of telematics solutions.
The Benefits of Telematics in Fleet Management
The adoption of telematics brings a myriad of benefits that can significantly impact a fleet’s bottom line and operational efficiency.
Operational Improvements
- Fuel Cost Reduction: Real-time monitoring of fuel consumption and driver behavior can lead to substantial savings.
- Enhanced Safety: By tracking driver behavior, fleets can identify and address risky driving practices.
- Increased Productivity: Optimized routing and reduced vehicle downtime lead to more efficient operations.
Specific Use Cases
- Asset Tracking: You can access real-time location data for all your fleet vehicles
- Maintenance Scheduling: Schedule predictive maintenance based on actual vehicle usage
- Insurance Risk Assessment: Usage-based insurance programs, which are expected to grow at a CAGR of 28.4%, rely heavily on telematics data
Customer Satisfaction and Regulatory Compliance
Telematics not only improves internal operations but also enhances the experience of your clients through more accurate delivery times and better service quality. Additionally, it helps in ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards, a critical aspect in today’s stringent regulatory environment.
Cost Considerations: Investing in Telematics
While the benefits of telematics are obvious, it’s crucial to understand the cost implications to make an informed decision.
Basic GPS Tracking vs. Integrated Solutions
Basic GPS tracking might be easier on your wallet initially and it does the job if you what you’re looking for is just the basics. However, if you’re looking for a comprehensive fully integrated solution that integrates seamlessly with your electronic logging devices, dash cams, and other fleet management solutions, then going for holistic telematics solution will give more more return on investment in the long run.
Factors Affecting Costs
- Device Types: The type of device used can significantly affect costs. This stems from the fact that there is a wide range of devices available – from simple GPS trackers which only provide location data, to advanced OBD-II devices that can monitor vehicle health, driver behaviour, and more. The sophistication and capabilities of the device will directly influence its price.
- Installation: Another factor to consider is whether you want to install the device yourself (DIY) or hire a professional to do it. DIY installation is typically cheaper, but it may not be feasible or safe for complex devices or large fleets. Professional installation, while more expensive, ensures that your devices are installed correctly and efficiently.
- Data Plans: The cost of data plans can vary greatly. It depends on the volume of data that needs to be transmitted and the frequency of transmission. A device that sends detailed reports every few minutes will require a more expensive plan than a device that only sends updates a few times a day.
- Software Subscriptions: Finally, the type of software subscription chosen will also affect costs. Subscriptions can range from basic reporting tools to advanced analytics platforms. The more comprehensive the data analysis and reporting capabilities, the higher the subscription cost.

Ensuring Data Security in Telematics
As telematics systems handle sensitive operational data, protecting against cyber threats and data breaches must become a top priority. Secure telematics systems safeguard not only your operational data but also your competitive edge in the market.
Best Practices for Telematics Security
- Implement end-to-end encryption for all data transmissions: As you integrate telematics into your operations, ensure that the system you choose uses robust encryption methods to protect your data.
- Carry out regular security audits and updates: Just like you routinely maintain your fleet vehicles, it’s important to regularly audit your telematics system for any security vulnerabilities. It’s a good practice to schedule these audits regularly to ensure your system remains secure.
- Establish strict access controls and user authentication: Not everyone should have access to your telematics data. Set up strict user access controls to keep sensitive information secure.
- Ensure compliance with data protection regulations: Depending on your location and the nature of your operations, different data protection laws may apply to your use of telematics. For example, in Europe, you’ll need to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). In Nigeria, your telematics systems must comply with the Nigerian Data Protection Act of 2023.
Industries Leveraging Telematics
Telematics applications extend far beyond traditional transportation sectors. Various industries are now harnessing the power of telematics to optimize their operations:
- Government: Fleet management for public services
- Heavy Equipment: Tracking and maintenance of construction machinery
- Public Safety: Optimizing emergency response times
- Truck Fleets: Enhancing logistics and delivery efficiency
- Construction: Improving site management and equipment utilization
- Oil & Gas: Monitoring remote assets and ensuring safety compliance
- Refrigeration: Maintaining temperature-sensitive cargo
- Mobile Service Providers: Optimizing field service operations
- Recreational Vehicles: Enhancing user experience and vehicle management
- Executive Fleets: Ensuring security and efficiency for corporate vehicles
The Future of Telematics: Emerging Technologies and Trends
The telematics industry continues to evolve rapidly, with new technologies shaping its future trajectory.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are set to revolutionize telematics by enabling:
- More accurate predictive maintenance
- Advanced route optimization algorithms
- Real-time risk assessment and mitigation
Growth Prospects
The telematics market shows no signs of slowing down. By 2030, global sales of telematics devices are expected to reach 200 million units annually, indicating robust growth opportunities for both providers and users of telematics solutions.
Future Applications
- Autonomous Vehicles: Telematics will play a crucial role in the development and operation of self-driving cars.
- Advanced Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems will predict failures with even greater accuracy, minimizing fleet downtime so that fleet operators can maximize profits.
- Enhanced Driver Assistance: Real-time feedback and coaching systems will further improve safety and efficiency with alerts, smart guidance, and so on.
Choosing the Right Telematics Solution
Selecting the appropriate telematics system is a critical step for any fleet manager. The wrong partner can entirely mess up your operations, costing you your reputation and wasted time and labour input.
Key Factors to Consider
- Scalability: Ensure that the system you choose can grow and scale with your fleet as it expands.
- Integration Capabilities: Look for solutions that can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems with flexibility for future upgrades.
- Customer Support: Reliable support is critical for smooth implementation and ongoing operations. Check the reviews of your provider to have an idea of what to expect.
- Data Analytics: Choose a platform with robust reporting and analysis tools. Data is the lifeblood of telematics. The more robust and useful the analytics are, the more value you get from the system.
Case Study: Learn How We Helped This Nigerian FMCG Company Improve Fleet Efficiency Dramatically

Embrace the Telematics Revolution
Telematics has evolved from a nice-to-have technology to an essential tool for fleet management. Its ability to provide real-time insights, improve operational efficiency, and enhance safety makes it indispensable in today’s competitive landscape.
As the aftermarket vehicle telematics segment grows at a CAGR of 15.4%, the opportunity for businesses to gain a competitive edge through advanced telematics solutions has never been greater.
By embracing telematics, you can move your fleet operations into a future of increased efficiency, improved safety, and enhanced profitability.
The telematics revolution is here. The question is not if you should adopt telematics, but how quickly you can leverage its power to transform your fleet operations.
MAXIMIZE YOUR FLEET’S EFFICIENCY WITH SALCOMMS TRACKERS